I have a laptop with a 500Gig SSD, but it’s too small. So I bought a 2TB SSD and replaced it. Here’s how I did it.
About the Laptop
The laptop is a Fujitsu U9311. To replace the SSD it was a matter of removing 10 screws from the bottom and lifting off the base. No clips to worry about. The SSD has a M.2 slot right there. The technical docs are available here.
Great job, Fujitsu, why did you stop making Laptops?
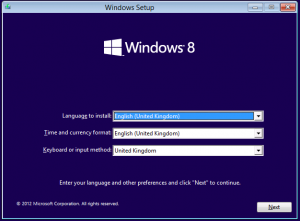
For reference, when booting, F2 will give the BIOS Setup. In setup I disabled Fast Boot so the Boot Menu is available.
Press F12 to get the boot menu.
Bitlocker considerations
I’ve replaced HDDs with SSDs a few times before, and upgraded SSDs as well. Without Bitlocker in the mix, the process is relatively straightforward (the process below is good for this, and you can also use gparted to expand the partitions).
With Bitlocker, I needed to know that the process wouldn’t interfere. It turns out that Windows is quite anti-fragile and you can do the things you would expect and it works.
The thing I didn’t risk is using a 3rd party tools to expand the Bitlocker partitions. That wasn’t a problem because Windows Disk Manager can expand a partition into any free space that exists after the partition.
Tools
The (free) software I used is openSUSE Leap KDE Rescue x86_64.iso which I copied onto a 2GB USB stick. This build boots on my laptop and contains the two tools I used:
- dd
- gparted
Process
- Put the new SSD in the Laptop
- Put the old SSD in a USB adapter
- Boot openSUSE
- Open Terminal and run
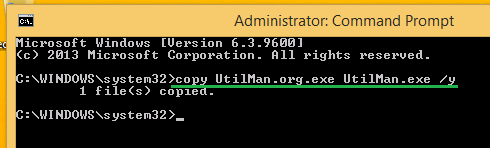
su - Check the devices (old was
/dev/sdb, new was/dev/nvme0n1) dd if=/dev/sdb of=/dev/nvme0n1- In another terminal (
su) find the process number of dd and watch progressps ax | grep ddwatch kill -n 30 -USR1 999
- Wait – I was copying 500GB onto a 2TB disk. It copied at 44Meg/s, so was about 3 hours.
- Remove the USBs (old and boot) and reboot to check everything still works. It did. No issues at all.
- Reboot into openSUSE
- Open Terminal and run
su, and thengparted. - Then, starting at the right hand end, move partitions to their new start positions (but don’t change the partition sizes).
- I have two partitions I wanted to expand: C: and E:. They were the 3rd and 5th partitions on the list, with partitions for EFI and Recovery there as well.
- If a partition is not to be expanded, move it as far right as it will go.
- If a partition is to be expanded, move it right and leave additional space to the right.
- The left-most partition to expand (C:), is left with free space after it.
- The actual move took about 3 minutes to move two small Recovery partitions and one 200Gig old partition.
- Reboot to Windows
- Using Disk Manager (Right click on My PC, Computer Management, Disk Manager), expand the partitions with free space after them.
- That’s it. No fussing, nothing unexpected.